EL FATEH PROJECTS LLC. ENGINEERING THE PRESENT, POWERING THE FUTURE

- EL Fateh Projects
- Solar Energy
Solar Energy

Harnessing the Power of the Sun for a Sustainable Future
As the green division of El Fateh Projects, Blocks Electric is at the forefront of driving sustainability across the Middle East and Africa. Our innovative solar energy solutions power everything from on–grid solar systems for residential, industrial, and commercial operations to off–grid setups providing reliable energy in remote locations. With our solar pump systems for agriculture, we bring eco–friendly and cost–effective water management to farming communities. Whether it’s solar panel installation or ongoing system maintenance, Blocks Electric delivers tailored solar solutions that reduce carbon footprints and support economic growth. Join the solar energy revolution with Blocks Electric and let us light your path to a greener and brighter future.
Key Benefits
Renewable Energy
Our deep understanding of renewable energy technologies allows us to provide customized solar solutions that meet your specific needs
Sustainability & Cost Savings
Solar energy reduces carbon emissions and offers significant long-term cost savings on energy bills.
Scalable Solar Solutions
We design scalable systems that can grow with your energy needs, from small-scale installations to large solar farms.
Solar Enegry Sub-Services
On-Grid Solar Systems
We design and install solar power systems that connect directly to the electrical grid, providing reliable and renewable energy for large-scale industrial and commercial applications.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
These Off-Grid Solar Systems are designed specifically for remote areas and standalone operations, we deliver off-grid solar solutions that provide independent and sustainable power.
Solar Pump Systems for Agriculture
Delivering sustainable water management solutions for agricultural needs & providing reliable irrigation and water supply in remote & rural areas
Maintenance and Optimization
We offer ongoing monitoring and maintenance services so that to ensure that your solar energy system continues to operate at it's peak efficiency.
Sub-Services Details
How it Works:
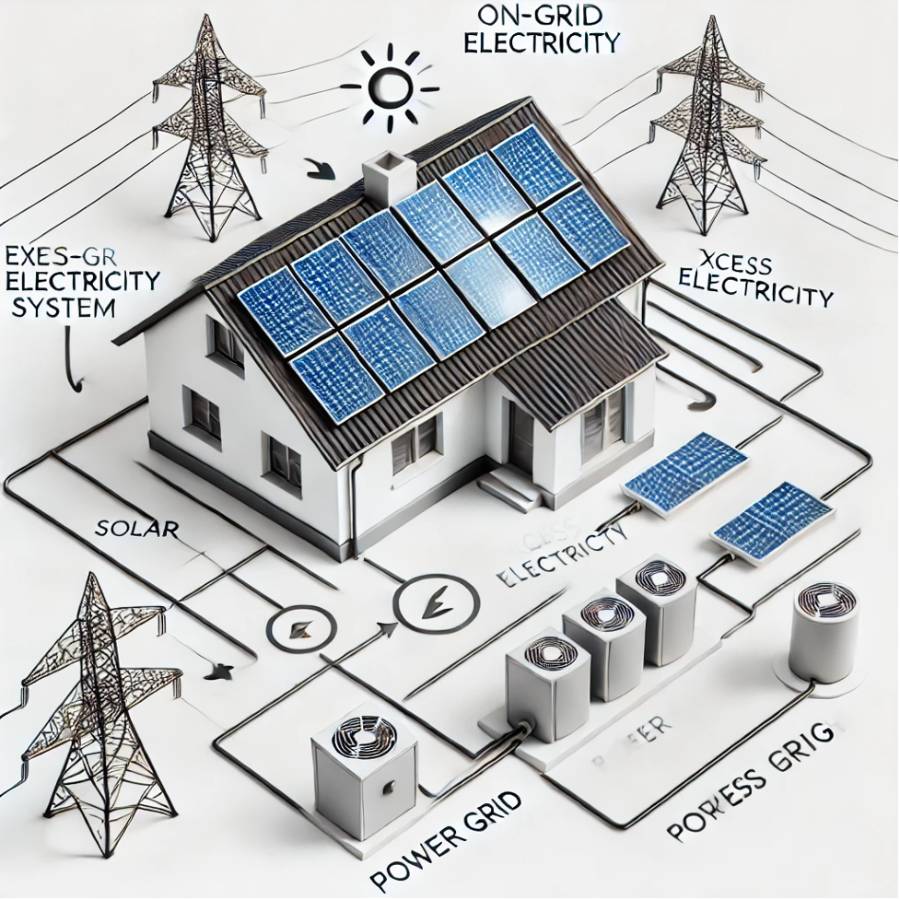
An on-grid solar system, or grid-tied system, generates electricity from solar panels and feeds it into the electrical grid. It converts sunlight into direct current (DC) through photovoltaic panels, which is then turned into alternating current (AC) by an inverter. The AC power is either used immediately or sent to the grid. Excess electricity is fed into the grid, and the utility may offer credits through net metering, lowering bills. When solar power is insufficient, the facility draws electricity from the grid to maintain a continuous supply.
Key Components:
• Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
• Inverter: Converts DC electricity into AC electricity.
• Net Metering: A system that credits owners for the excess electricity they send to the grid.
• Electrical Grid: The solar system is connected to the grid, which acts as storage.
Technical Benefits:
• Cost Savings: Reduced electricity bills through net metering.
• No Battery Dependency: Since the grid acts as backup, batteries are not needed.
• Scalability: On-grid systems can easily be expanded by adding more panels.
Use Cases:
• Ideal for locations with stable grid infrastructure.
• Commercial and industrial projects benefit from the reliability of the grid while reducing electricity costs.
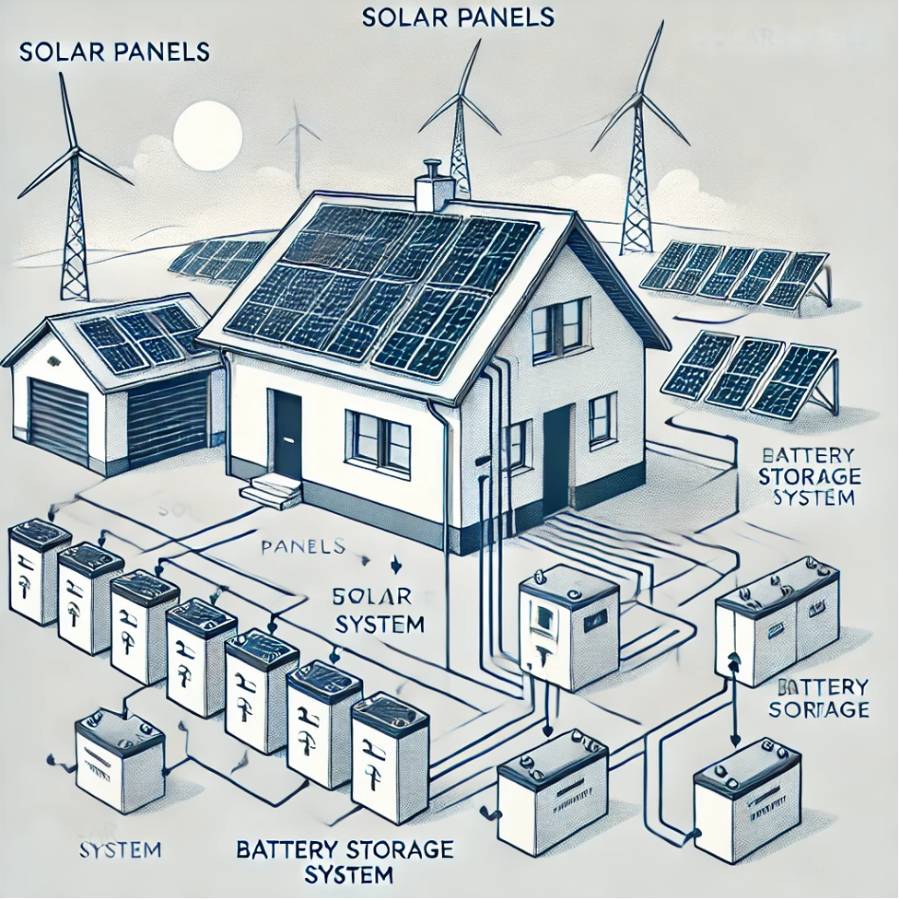
How it Works:
An off-grid solar system is entirely self-sufficient and does not rely on the electrical grid. It generates electricity from solar panels in a similar way to on-grid systems but stores excess energy in batteries for later use. This allows the system to provide continuous power even when the sun is not shining, such as during the night or cloudy days. Electricity is generated from the solar panels and sent to a charge controller, which regulates the voltage and current going to the battery bank to ensure efficient charging and protect the batteries from overcharging. When electricity is needed, it is drawn from the battery and passed through an inverter, which converts the stored DC power into AC electricity for use in homes or businesses.
Key Components:
• Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
• Charge Controller: Ensures the batteries are charged efficiently without damage.
• Battery Bank: Stores excess electricity for use when solar power is not available.
• Inverter: Converts DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity for use in appliances.
Technical Benefits:
• Energy Independence: Not reliant on the grid, providing power in remote locations.
• Sustainability: Provides renewable, clean energy 24/7 with stored power.
• Backup Power: Batteries provide backup power during outages or nighttime.
Use Cases:
• Best suited for remote areas without access to the electrical grid.
• Ideal for isolated cabins, rural homes, and off-grid businesses.
• Provides reliable power for standalone operations in extreme conditions.
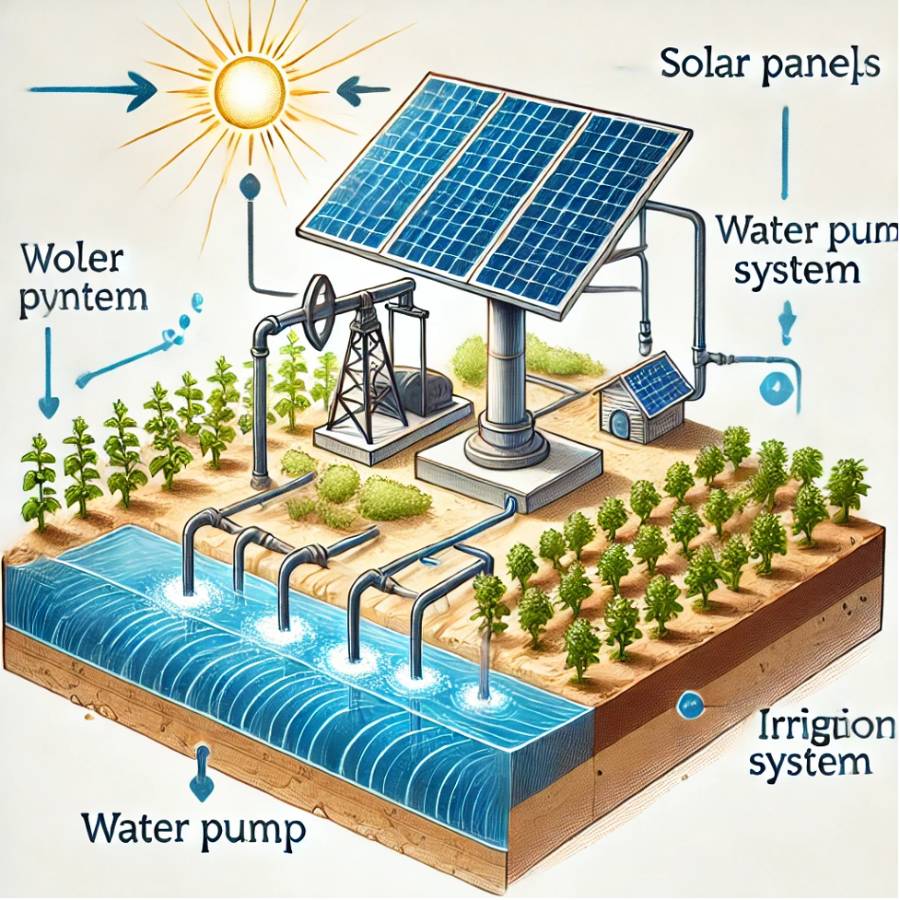
How it Works:
A solar pump system uses solar energy to power water pumps for irrigation and water supply. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which drives an electric motor connected to the pump. This setup can draw water from sources like wells or ponds, ideal for areas without grid access. It typically includes solar panels, an electric motor, a pump, and an irrigation system. Water can be stored or distributed directly to fields. Some systems have controllers to optimize operation and may include batteries for consistent water supply during low sunlight.
Key Components:
• Solar Panels: Capture sunlight to generate electricity for the pump.
• Water Pump: Powered by solar energy, it draws water from a source (well, river, etc.).
• Irrigation System: Delivers water to the crops efficiently, either directly or via storage tanks.
• Controller (optional): Manages water flow and adjusts pump operation based on solar input and water needs.
Technical Benefits:
• Cost-Effective: Reduces reliance on diesel pumps or grid power, lowering operational costs.
• Eco-Friendly: Solar-powered pumps produce no greenhouse gas emissions.
• Reliable Water Supply: Provides a consistent and reliable water source for agriculture, especially in remote or off-grid locations.
• Scalable: Can be designed to fit small farms or large-scale agricultural operations.
Use Cases:
• Ideal for remote farming communities without access to electricity.
• Provides a sustainable irrigation solution for small- and large-scale farming.
• Ensures reliable water supply in areas where grid power or diesel is expensive or unreliable.